Endothelial dysfunction might be due to uncoupled eNOS. Several studies have shown that relaxin effects are endothelium and NO dependent. Thus, impaired endothelium mediated vascular relaxation in the dTGR model could explain the missing relaxin effectiveness. Recently Parikh et al. showed beneficial effects of relaxin on Eleutheroside-E atrial fibrillation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Relaxin treatment reversed the transcripts for fibrosis, increasing conduction velocity, reduced electrophysiological abnormalities, and reversed atrial hypertrophy. In their study a one-week therapy was ineffective in suppressing atrial 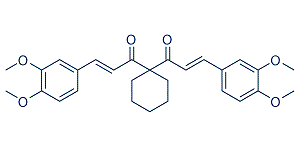 fibrillation and longer relaxin treatment was necessary. The authors speculate that reversal of fibrosis is a slow process as a result of the slow collagen turnover rate of around 5% per day in healthy hearts. The fibrosis in our dTGR is much more pronounced. This state-of-affairs and the fact that fibrosis accelerates over time might be the reason why relaxin was not successful in ameliorating target-organ damage in dTGR. We were also interested in the kidney in dTGR. Recently Yoshida et al demonstrated that relaxin protected against ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury by reducing apoptosis and inflammation. Relaxin also preserved renal function in their model. Their relaxin dose, namely 500 ng/h was higher than our high-dose. Moreover, the design of their study was based on acute renal failure; our study was chronic in nature. Parikh et al did not investigate inflammation, while Yoshida et al showed that the TNFa receptor-1 was up regulated in the kidney and normalized by relaxin. We found no such effects in dTGR model. The transcription factors nuclear factor-kB and activator-protein 1 are strongly activated and responsible for the sustained inflammatory and proliferative response in this model. Macrophages, dendritic cells and CD4 and CD8 T cells are strongly activated. Surface adhesion molecule expression, such as ICAM-1, VCAM-1, TNFa and interleukin-6, tissue factor production, and activation of enzymes producing reactive oxygen species are highly induced. We speculate that relaxins anti-inflammatory potential was not sufficient to counteract the pro-inflammatory storm in dTGR. In contrast to our findings, Lekgabe et al. showed that relaxin reduced target-organ damage in spontaneous hypertensive rats. However, end-organ damage takes 9�C10 months to develop in that model and is far less severe than the effects reported here. Relaxin, applied for 2 weeks, normalized fibrosis in heart and kidney, inhibited cell and increased MMP-2 expression. Blood pressure was not affected by relaxin treatment and mortality was not investigated. Wong et al investigated the effects of relaxin on fibrosis in streptozotocin -treated transgenic mRen-2 rats. That model is also Ang II-mediated and features fairly severe changes. Relaxin did not ameliorate glomerulopathy in this accelerated model of type 1 diabetes. Relaxin did not reduce Saikosaponin-B2 hypertension or albuminuria. Similar to our study, the authors were puzzled by the negative results. The authors observed that relaxin was very successful in reversing fibrosis when the TGF-b1 pathway was activated and subsequently phosphorylation and down regulation of smad-2 occurred. This was not the case in the dTGR.
fibrillation and longer relaxin treatment was necessary. The authors speculate that reversal of fibrosis is a slow process as a result of the slow collagen turnover rate of around 5% per day in healthy hearts. The fibrosis in our dTGR is much more pronounced. This state-of-affairs and the fact that fibrosis accelerates over time might be the reason why relaxin was not successful in ameliorating target-organ damage in dTGR. We were also interested in the kidney in dTGR. Recently Yoshida et al demonstrated that relaxin protected against ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury by reducing apoptosis and inflammation. Relaxin also preserved renal function in their model. Their relaxin dose, namely 500 ng/h was higher than our high-dose. Moreover, the design of their study was based on acute renal failure; our study was chronic in nature. Parikh et al did not investigate inflammation, while Yoshida et al showed that the TNFa receptor-1 was up regulated in the kidney and normalized by relaxin. We found no such effects in dTGR model. The transcription factors nuclear factor-kB and activator-protein 1 are strongly activated and responsible for the sustained inflammatory and proliferative response in this model. Macrophages, dendritic cells and CD4 and CD8 T cells are strongly activated. Surface adhesion molecule expression, such as ICAM-1, VCAM-1, TNFa and interleukin-6, tissue factor production, and activation of enzymes producing reactive oxygen species are highly induced. We speculate that relaxins anti-inflammatory potential was not sufficient to counteract the pro-inflammatory storm in dTGR. In contrast to our findings, Lekgabe et al. showed that relaxin reduced target-organ damage in spontaneous hypertensive rats. However, end-organ damage takes 9�C10 months to develop in that model and is far less severe than the effects reported here. Relaxin, applied for 2 weeks, normalized fibrosis in heart and kidney, inhibited cell and increased MMP-2 expression. Blood pressure was not affected by relaxin treatment and mortality was not investigated. Wong et al investigated the effects of relaxin on fibrosis in streptozotocin -treated transgenic mRen-2 rats. That model is also Ang II-mediated and features fairly severe changes. Relaxin did not ameliorate glomerulopathy in this accelerated model of type 1 diabetes. Relaxin did not reduce Saikosaponin-B2 hypertension or albuminuria. Similar to our study, the authors were puzzled by the negative results. The authors observed that relaxin was very successful in reversing fibrosis when the TGF-b1 pathway was activated and subsequently phosphorylation and down regulation of smad-2 occurred. This was not the case in the dTGR.
Month: April 2019
It is easy to perform in clinical practice and could be helpful in determining therapeutic regimens for GBM
Aminopeptidases exist widely in prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbial species, which can selectively catalyze the cleavage of the N-terminal amino acid residues from peptides and proteins. APs are associated with many human diseases and play an important role in a wide range of biological processes. The research to elucidate the catalytic mechanisms of APs is significant for medicine and pharmacology. APs have great application in various fields because of their broad substrate specificity, strict enantioselectivity, and high thermal stability. Besides being applied to synthesize pharmaceutical compounds and acting as versatile chiral building blocks, they are mainly applied in 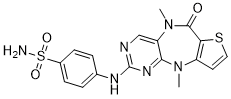 the food industry. For instance, APs play an important role in debittering protein hydrolysate and increasing the content of free amino acids in protein hydrolysate. They are also used as additives in condiments, such as soy sauce and seasoning blends, to enhance the flavor and the nutritional value of foods. Based on the homology modeling and structure analysis of BSAP, we found that there was a protease-associated Gomisin-D domain in the non-catalytic region. The PA domain is about 150 amino acids long, containing two a-helices and seven b-sheets. Because this domain is found in several distinct Procyanidin-B1 classes of proteases, it was named PA domain. Besides the different protease families, this domain was also found in two classes of plant transmembrane proteins. However, the role of PA domain remains somewhat elusive. It has been speculated that PA domain was involved in protein-protein interaction. In M28 family, the PA domain was found in only a few APs and the role of PA domain in APs has not been reported yet. Herein we found that the PA domain showed much more flexibility than any other regions in BSAP by using molecular dynamics simulation. The structure of the hypothetical deleted form of BSAPDPA was modeled and analyzed using MDS, and it was predicted that deletion of this flexible domain can enhance the structure stability. In vivo, the enzymatic reaction is an important biological process that can serve a wide variety of purposes. Inappropriate activity of enzymes can be deleterious to the cell or the organism that produces them. Thus, many enzymes contain conserved domains that can serve as an auto-inhibitor, a substrate-targeting domain or a regulatory domain, allowing catalysis events to occur only in the correct subcellular compartment, at the correct time and with the correct substrates. However, in the industrial application of the enzymes, sometimes these regulatory domains were unnecessary or even detrimental to the catalytic process. In order to satisfy the industrial requirement, it was an efficient approach to reconstruct the enzymes via deletion of these redundant regions. It has been reported that truncation of the cellulose binding domain of glucanase improved its thermal stability. Recently, Xiangtao Liu et al reported that N-terminal truncation of a maleate cis-trans isomerase resulted in a highly active enzyme for the biocatalytic production of fumaric acid. The research about changing optimum pH of an invertase by N-terminal truncation was also reported.
the food industry. For instance, APs play an important role in debittering protein hydrolysate and increasing the content of free amino acids in protein hydrolysate. They are also used as additives in condiments, such as soy sauce and seasoning blends, to enhance the flavor and the nutritional value of foods. Based on the homology modeling and structure analysis of BSAP, we found that there was a protease-associated Gomisin-D domain in the non-catalytic region. The PA domain is about 150 amino acids long, containing two a-helices and seven b-sheets. Because this domain is found in several distinct Procyanidin-B1 classes of proteases, it was named PA domain. Besides the different protease families, this domain was also found in two classes of plant transmembrane proteins. However, the role of PA domain remains somewhat elusive. It has been speculated that PA domain was involved in protein-protein interaction. In M28 family, the PA domain was found in only a few APs and the role of PA domain in APs has not been reported yet. Herein we found that the PA domain showed much more flexibility than any other regions in BSAP by using molecular dynamics simulation. The structure of the hypothetical deleted form of BSAPDPA was modeled and analyzed using MDS, and it was predicted that deletion of this flexible domain can enhance the structure stability. In vivo, the enzymatic reaction is an important biological process that can serve a wide variety of purposes. Inappropriate activity of enzymes can be deleterious to the cell or the organism that produces them. Thus, many enzymes contain conserved domains that can serve as an auto-inhibitor, a substrate-targeting domain or a regulatory domain, allowing catalysis events to occur only in the correct subcellular compartment, at the correct time and with the correct substrates. However, in the industrial application of the enzymes, sometimes these regulatory domains were unnecessary or even detrimental to the catalytic process. In order to satisfy the industrial requirement, it was an efficient approach to reconstruct the enzymes via deletion of these redundant regions. It has been reported that truncation of the cellulose binding domain of glucanase improved its thermal stability. Recently, Xiangtao Liu et al reported that N-terminal truncation of a maleate cis-trans isomerase resulted in a highly active enzyme for the biocatalytic production of fumaric acid. The research about changing optimum pH of an invertase by N-terminal truncation was also reported.
Association between MYCL and systolic left-ventricular function in the T2DM-group
However, the ejection fraction did not differ between the groups. The link between myocardial lipids and systolic function is of interest, since myocardial lipid accumulation has been linked to the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy triggered 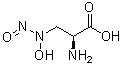 by lipotoxicity. Until now, our knowledge mainly relies on animal data, and recent reports have focused on the quality rather than the quantity of myocardial lipids; there is evidence that in particular saturated free fatty acids might favor the development of cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction, while unsaturated free fatty acids might play a protective role. Hence, it can be speculated that the assessment of lipid composition rather than quantification of triglycerides in the heart alone, might help to draw a link between myocardial lipid accumulation and cardiac dysfunction. In our current study, we found that besides blood pressure, myocardial wall thickness was tightly associated with BMI, glycemic control, hyperinsulinemia and hsCRP. Again, we think that long-term exposure to these co-existing risk factors might accelerate the development of myocardial hypertrophy in patients with diabetes. In contrast to myocardial lipids, hepatic steatosis, estimated by the Fatty Liver Index, was tightly correlated with metabolic parameters: glycemic control, hyperinsulinemia as well as dyslipidemia. In a recent study in women with prior gestational diabetes, hepatic lipid content was doubled in pGDM compared to healthy controls and tightly associated with insulin resistance. Thus, we conclude that hepatic lipid accumulation better Ganoderic-acid-F reflects glucometabolic alterations than do myocardial lipids. This could be explained by a higher turnover of the myocardial lipid pool compared to that of the liver. There are some study limitations that have to be addressed. First of all, the study group is rather small in terms of participants, due to the difficulty of recruitment from the long-lasting project with a well-characterized cohort and the cost- and time-consuming examinations. Secondly, we investigated a quite young, premenopausal female population, whose cardiovascular risk factors might still be low to detect relevant changes. Furthermore, diastolic function is only described by the E/A-ratio, which might limit our conclusions on diastolic function. Breast cancer is the most common malignancy among women in the United States, among which 70% of them are ER+. The selective ER modulator tamoxifen has shown great success in the treatment of ER+ breast cancer. However, over 40% ER+ patients with advanced disease fail to respond to tamoxifen effectively, even for those who responded at the beginning would develop acquired resistance eventually. Approximately 25% of all women diagnosed with breast cancer die from their disease despite having been treated according to state-of-the-art clinical guidelines. In the meantime, adjuvant systemic therapy saves a significant number of lives, however, many patients are subjected to unnecessary adjuvant therapies with the potential of causing more harm than good. The present lack of criteria to help Echinacoside individualize breast cancer treatment indicates the need for a novel way to predict prognosis and therapy response.
by lipotoxicity. Until now, our knowledge mainly relies on animal data, and recent reports have focused on the quality rather than the quantity of myocardial lipids; there is evidence that in particular saturated free fatty acids might favor the development of cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction, while unsaturated free fatty acids might play a protective role. Hence, it can be speculated that the assessment of lipid composition rather than quantification of triglycerides in the heart alone, might help to draw a link between myocardial lipid accumulation and cardiac dysfunction. In our current study, we found that besides blood pressure, myocardial wall thickness was tightly associated with BMI, glycemic control, hyperinsulinemia and hsCRP. Again, we think that long-term exposure to these co-existing risk factors might accelerate the development of myocardial hypertrophy in patients with diabetes. In contrast to myocardial lipids, hepatic steatosis, estimated by the Fatty Liver Index, was tightly correlated with metabolic parameters: glycemic control, hyperinsulinemia as well as dyslipidemia. In a recent study in women with prior gestational diabetes, hepatic lipid content was doubled in pGDM compared to healthy controls and tightly associated with insulin resistance. Thus, we conclude that hepatic lipid accumulation better Ganoderic-acid-F reflects glucometabolic alterations than do myocardial lipids. This could be explained by a higher turnover of the myocardial lipid pool compared to that of the liver. There are some study limitations that have to be addressed. First of all, the study group is rather small in terms of participants, due to the difficulty of recruitment from the long-lasting project with a well-characterized cohort and the cost- and time-consuming examinations. Secondly, we investigated a quite young, premenopausal female population, whose cardiovascular risk factors might still be low to detect relevant changes. Furthermore, diastolic function is only described by the E/A-ratio, which might limit our conclusions on diastolic function. Breast cancer is the most common malignancy among women in the United States, among which 70% of them are ER+. The selective ER modulator tamoxifen has shown great success in the treatment of ER+ breast cancer. However, over 40% ER+ patients with advanced disease fail to respond to tamoxifen effectively, even for those who responded at the beginning would develop acquired resistance eventually. Approximately 25% of all women diagnosed with breast cancer die from their disease despite having been treated according to state-of-the-art clinical guidelines. In the meantime, adjuvant systemic therapy saves a significant number of lives, however, many patients are subjected to unnecessary adjuvant therapies with the potential of causing more harm than good. The present lack of criteria to help Echinacoside individualize breast cancer treatment indicates the need for a novel way to predict prognosis and therapy response.
We analyzed the association of miR-630 with clinicopathological characteristics as well as prognosis of patients
Results showed that Tenuifoliside-C miR-630 expression was increased in gastric cancer compared with that in adjacent and normal control tissues for high expression of miR-630 was more likely to be detected in gastric cancer specimens, which indicating its possible participation on carcinogenesis. It is also found that miR-630 expression was closely related to gastric cancer invasion, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and TNM stage 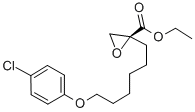 for high expression of miR-630 was more frequently to be detected in tumors with deep invasion, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis or advanced TNM stage, suggesting the possible participation of miR-630 on gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Together with the above evidence, it was thus proposed that miR-630 may play important roles in gastric cancer carcinogenesis and progression. As miR-630 expression was found to be associated with gastric cancer invasion and metastasis, considering the invasion of cancer to nearby tissues and metastasis to distal tissues are crucial factors affecting the prognosis of patients, miR-630 might be a potential prognostic marker for Isochlorogenic-acid-C patients with gastric cancer. In order to investigate the prognostic role of miR-630 on gastric cancer, we performed Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival. Results showed that patients with gastric cancer of high miR-630 expression tend to have worse overall survival in comparison to patients with tumor of low miR-630 expression, which suggested that miR-630 expression was a prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer. To further evaluate the prognostic value of miR630 in gastric cancer, we performed Cox proportional hazards model which was adjusted for gender, age and TNM stage of patients. Results proved that increased miR-630 expression was a marker of poor overall survival independent of adjusted factors, thus, miR-630 could be utilized to determine patients’ prognosis with out considering TNM stage. These results indicated that miR-630 could constitute a molecular prognostic marker additive to TNM stage for patients with gastric cancer, identifying high risk individuals who are more likely to have tumor relapse in clinical practice, thus, good candidates to receive more aggressive treatment. These results were in consistent with investigations focused on non-small cell lung cancer, indicating the consistence of miR-630 function in these types of tumor. Thus, the positive linkage between miR-630 overexpression and poor prognosis may not only be used for identifying gastric cancer patients with higher risk of early tumor relapse but also for providing valuable clues to understand the possible mechanism of gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. In conclusion, we have proved that miR-630 expression was increased in gastric cancer and associated with tumor progression. The present study also demonstrated for the first time that miR630 expression was an independent prognostic factor of patients with gastric cancer. Therefore, it is possible that miR-630 may play an important role in invasiveness and metastasis of gastric cancer. It is also possible that miR-630 serves as prognostic marker in clinical practice and even the inhibition for miR-630 using specific inhibitors may become a new therapeutic.
for high expression of miR-630 was more frequently to be detected in tumors with deep invasion, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis or advanced TNM stage, suggesting the possible participation of miR-630 on gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Together with the above evidence, it was thus proposed that miR-630 may play important roles in gastric cancer carcinogenesis and progression. As miR-630 expression was found to be associated with gastric cancer invasion and metastasis, considering the invasion of cancer to nearby tissues and metastasis to distal tissues are crucial factors affecting the prognosis of patients, miR-630 might be a potential prognostic marker for Isochlorogenic-acid-C patients with gastric cancer. In order to investigate the prognostic role of miR-630 on gastric cancer, we performed Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival. Results showed that patients with gastric cancer of high miR-630 expression tend to have worse overall survival in comparison to patients with tumor of low miR-630 expression, which suggested that miR-630 expression was a prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer. To further evaluate the prognostic value of miR630 in gastric cancer, we performed Cox proportional hazards model which was adjusted for gender, age and TNM stage of patients. Results proved that increased miR-630 expression was a marker of poor overall survival independent of adjusted factors, thus, miR-630 could be utilized to determine patients’ prognosis with out considering TNM stage. These results indicated that miR-630 could constitute a molecular prognostic marker additive to TNM stage for patients with gastric cancer, identifying high risk individuals who are more likely to have tumor relapse in clinical practice, thus, good candidates to receive more aggressive treatment. These results were in consistent with investigations focused on non-small cell lung cancer, indicating the consistence of miR-630 function in these types of tumor. Thus, the positive linkage between miR-630 overexpression and poor prognosis may not only be used for identifying gastric cancer patients with higher risk of early tumor relapse but also for providing valuable clues to understand the possible mechanism of gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. In conclusion, we have proved that miR-630 expression was increased in gastric cancer and associated with tumor progression. The present study also demonstrated for the first time that miR630 expression was an independent prognostic factor of patients with gastric cancer. Therefore, it is possible that miR-630 may play an important role in invasiveness and metastasis of gastric cancer. It is also possible that miR-630 serves as prognostic marker in clinical practice and even the inhibition for miR-630 using specific inhibitors may become a new therapeutic.
Important functional as the alanine mutations of the charge reversal on K221 could abolish
These results support the model of the ATPase cycle, according to which the thermal movements of the lid segment may open up the conformational space for the catalytic Arg residue from the Hsp90-MD to reach the nucleotide binding site and induce ATP hydrolysis. Although the lack of structural information about the full Hsp90 dimer interacting Sgt1 and Rar1 precludes direct modeling of this mechanism, our results point to the key role of Rar1-CHORD2 as an allosteric regulator of the lid dynamics. Rather interestingly, despite a considerable lid flexibility in the ternary complex, the lid movements in each of the Hsp90-NTD could be correlated with the functional displacements of the interacting Sgt1-CS and Rar1-CHORD2 domains. Hence, in contrast to the binary complex, functional dynamics of the Hsp90-Sgt1-Rar1 assembly may be characterized by correlated motions of the interacting molecules. These findings are consistent with the experiments suggesting that RAR1-CHORD2 facilitates cooperative assembly of the complex and can enhance the ATPase activity while destabilizing the closed lid conformation. According to previous studies structural plasticity and functional 9-methoxycamptothecine adaptation of Hsp90 to the vastly divergent families of interacting cochaperones and client proteins are enabled by modulating the proper balance of structural rigidity and flexibility in the Hsp90 interdomain interfaces. We have recently demonstrated that functionally important regulatory sites of Hsp90 may be strategically positioned at the interdomain regions separating structurally rigid and flexible regions. These Procyanidin-B1 residues often correspond to hinge sites around which large protein movements are organized. In this section, we analyzed how cochaperonemediated modulation of the Hsp90 dynamics could affect the distribution of structural rigid and flexible regions that are crucial for proper functioning of the chaperone. Using the force constant method within the framework of the discrete molecular dynamics formalism as implemented in we computed the fluctuation distance force constant for each residue in the Hsp90-Sgt1 and Hsp90-Sgt1-Rar1 complexes. The highest sharp peaks in force constant distributions are typically associated with the residues forming boundaries between structurally rigid and flexible regions, and could indicate the interdomain hinge sites. The residue-based force constant profiles of the Hsp90-Sgt1 and Hsp90-Sgt1-Rar1 complexes are characterized by several high value peaks separating structurally rigid and flexible residues. Interestingly, the most notable sharpest peaks that signify an abrupt transition from structurally stable to mobile regions were observed near the lid motif of the Hsp90-NTD. In the Hsp90-Sgt1 complex, the pronounced peak corresponds to the L95 residue that anchors one end of the lid motif and F126 that anchors the opposite end of the lid. Only a few very minor peaks could be spotted in the Sgt1-CS  domain, corresponding to a stretch of structurally immobilized residues at the intermolecular Hsp90-Sgt1 interface. Consistent with the ENM-based analysis, the force constant profile of the binary Hsp90-Sgt1 complex similarly indicated the greater mobility of the Sgt1-CS domain. The residue-based dynamic profiles are based on the consecutive residue numbering for the Hsp90-NTD and Sgt1-CS domains in the complex. For clarity of the comparison with structural and functional experiments, we refer to the important functional residues according to their original numbering in the crystal structures. We observed three distinctive peaks in the Sgt1CS domain profile corresponding respectively to Y157, F168, and K221 residues.
domain, corresponding to a stretch of structurally immobilized residues at the intermolecular Hsp90-Sgt1 interface. Consistent with the ENM-based analysis, the force constant profile of the binary Hsp90-Sgt1 complex similarly indicated the greater mobility of the Sgt1-CS domain. The residue-based dynamic profiles are based on the consecutive residue numbering for the Hsp90-NTD and Sgt1-CS domains in the complex. For clarity of the comparison with structural and functional experiments, we refer to the important functional residues according to their original numbering in the crystal structures. We observed three distinctive peaks in the Sgt1CS domain profile corresponding respectively to Y157, F168, and K221 residues.