The knowledge of genes and pathways involved in disease is of great importance to understand the pathogenic mechanisms of disease, and consequently to improve therapy, diagnosis and disease prevention. Linkage and association studies in human are commonly used to identify candidate susceptibility loci in Mendelian disorder. However, the heterogeneity of the human genome, the minor single gene contribution to the pathogenesis, and the multiplex gene-gene and gene-environment interactions render challenging to identify genes with low effect in complex disease. Therefore, animal models are invaluable tools to decipher genetic factors affecting quantitative traits, since they allow us to control the genetic background and to define the environmental conditions. It is highly toxic 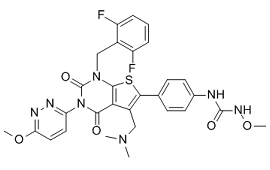 to humans and is associated with high mortality, mainly as a consequence of respiratory failure. The most common poisoning route is by ingestion of the concentrated solution, either intentional or accidental. On rare occasions, there are also cases of intoxication by way of dermal exposure or intravenous AbMole 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid injections. Dermal exposure reportedly results in severe PQ poisoning, especially in the presence of pre-existing skin lesions. Intravenous PQ poisoning is rare, and the clinical presentation and prognosis of such a scenario would be quite different from that of oral ingestion. Plasma PQ levels peak at two hr after PQ ingestion and decrease rapidly. PQ is eliminated by the kidney in urine. Severe PQ poisoning is characterized by multiple-organ failure, which mainly involves the lungs, kidneys, liver, heart and also the nervous system. The lung is a major target organ in paraquat poisoning, and respiratory failure from lung injury is the most common cause of death. The exact mechanism of PQ poisoning is currently unknown. Because of a lack of effective antidotes, conventional supportive treatments are poor and have a high mortality rate. Many scholars are devoted to this subject. Pulse AbMole Capromorelin tartrate therapy with cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone has significantly prevented pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Endothelin is an endothelium-derived 21-residue vasoconstrictor peptide. It was isolated by a Japanese scholar in 1988, and has been shown to be one of the most potent known vasoconstrictors. The ETs have three distinct isoforms, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo, and it is the only one that is constitutively released by the vascular endothelium. In addition, ET-1 is also produced by smooth muscle cells, macrophages, airway epithelium, and alveolar epithelial cells. ET-1 is released following various injurious stimuli, including shear stress, thrombin, angiotensin II, cytokines, and free radicals.
to humans and is associated with high mortality, mainly as a consequence of respiratory failure. The most common poisoning route is by ingestion of the concentrated solution, either intentional or accidental. On rare occasions, there are also cases of intoxication by way of dermal exposure or intravenous AbMole 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid injections. Dermal exposure reportedly results in severe PQ poisoning, especially in the presence of pre-existing skin lesions. Intravenous PQ poisoning is rare, and the clinical presentation and prognosis of such a scenario would be quite different from that of oral ingestion. Plasma PQ levels peak at two hr after PQ ingestion and decrease rapidly. PQ is eliminated by the kidney in urine. Severe PQ poisoning is characterized by multiple-organ failure, which mainly involves the lungs, kidneys, liver, heart and also the nervous system. The lung is a major target organ in paraquat poisoning, and respiratory failure from lung injury is the most common cause of death. The exact mechanism of PQ poisoning is currently unknown. Because of a lack of effective antidotes, conventional supportive treatments are poor and have a high mortality rate. Many scholars are devoted to this subject. Pulse AbMole Capromorelin tartrate therapy with cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone has significantly prevented pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Endothelin is an endothelium-derived 21-residue vasoconstrictor peptide. It was isolated by a Japanese scholar in 1988, and has been shown to be one of the most potent known vasoconstrictors. The ETs have three distinct isoforms, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo, and it is the only one that is constitutively released by the vascular endothelium. In addition, ET-1 is also produced by smooth muscle cells, macrophages, airway epithelium, and alveolar epithelial cells. ET-1 is released following various injurious stimuli, including shear stress, thrombin, angiotensin II, cytokines, and free radicals.
Month: April 2019
Bosentan therapy has shown to increase susceptibility to infection no symptoms of infection were observed
Differentiation, contraction, and AbMole Ellipticine collagen synthesis. It also independently 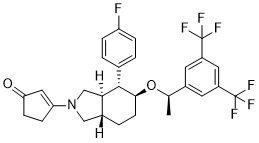 promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The plasma ET levels in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than those of the AbMole Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate controls. Bosentan is a dual endothelin-receptor antagonist that can be taken orally, and in patients with severe PH, it can improve exercise capacity, hemodynamics and quality of life. Bosentan application to bleomycin-treated rats resulted in significantly higher exercise capacity as a result of improvements in PH and PF and improvements in their quality of life. The present data suggests a therapeutic utility for bosentan, particularly in treating the early stages of chronic inflammatory airway diseases. The present study was designed to evaluate the effects of bosentan as a PQ poisoning treatment. Over the past few years, cytokine research has brought new ideas to PQ therapy. TGF-b1 is a multifunction cytokine; it can stimulate the proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, synthesize extracellular matrix and suppress collagen degradation, promote collagen deposition, and it may then play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of PF. One domestic study found that the level of caveolin-1 decreased in rats after PQ exposure. Caveolin-1 notably downregulates transforming growth factor-b signal transduction by modulating TGF-b1 receptor gene expression, preventing Smad2 phosphorylation, and/or mediating TGF-b receptor turnover. ET-1 also plays a central role in lung fibrosis. ET-1 has been shown to induce fibroblast proliferation, differentiation, contraction, and collagen synthesis. It also independently promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The levels of plasma ET in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than in the controls. An ETA receptor antagonist was shown to inhibit the development of paraquat-induced PF, confirming the importance of ET-1 in mediating PF in a rat experiment. There are three distinct isoforms endothelins, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3 and two endothelin receptors, namely ETA-R and ETB-R. ETA-R mainly resides in smooth muscle cells, and ETB-R is in the endotheliocyte. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo one of the two receptors. Bosentan is a nonselective dual endothelin-receptor antagonist, and it is widely used to treat PH. It can improve the exercise capacity and hemodynamics of PH patients. In recent years, bosentan has been shown to have some function in acute lung injury and PF by three methods, which included reducing the right ventricular systolic pressure, decreasing reactive oxygen species release and relieving the inflammatory reaction.
promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The plasma ET levels in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than those of the AbMole Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate controls. Bosentan is a dual endothelin-receptor antagonist that can be taken orally, and in patients with severe PH, it can improve exercise capacity, hemodynamics and quality of life. Bosentan application to bleomycin-treated rats resulted in significantly higher exercise capacity as a result of improvements in PH and PF and improvements in their quality of life. The present data suggests a therapeutic utility for bosentan, particularly in treating the early stages of chronic inflammatory airway diseases. The present study was designed to evaluate the effects of bosentan as a PQ poisoning treatment. Over the past few years, cytokine research has brought new ideas to PQ therapy. TGF-b1 is a multifunction cytokine; it can stimulate the proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, synthesize extracellular matrix and suppress collagen degradation, promote collagen deposition, and it may then play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of PF. One domestic study found that the level of caveolin-1 decreased in rats after PQ exposure. Caveolin-1 notably downregulates transforming growth factor-b signal transduction by modulating TGF-b1 receptor gene expression, preventing Smad2 phosphorylation, and/or mediating TGF-b receptor turnover. ET-1 also plays a central role in lung fibrosis. ET-1 has been shown to induce fibroblast proliferation, differentiation, contraction, and collagen synthesis. It also independently promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The levels of plasma ET in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than in the controls. An ETA receptor antagonist was shown to inhibit the development of paraquat-induced PF, confirming the importance of ET-1 in mediating PF in a rat experiment. There are three distinct isoforms endothelins, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3 and two endothelin receptors, namely ETA-R and ETB-R. ETA-R mainly resides in smooth muscle cells, and ETB-R is in the endotheliocyte. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo one of the two receptors. Bosentan is a nonselective dual endothelin-receptor antagonist, and it is widely used to treat PH. It can improve the exercise capacity and hemodynamics of PH patients. In recent years, bosentan has been shown to have some function in acute lung injury and PF by three methods, which included reducing the right ventricular systolic pressure, decreasing reactive oxygen species release and relieving the inflammatory reaction.
More recent evidence indicates the intestinal stem cells are relatively insensitive to a reduction in Wnt secretion
Finally, it has been shown that Wls is a Wnt target gene in the mouse. By stimulating the expression of Wls, secretion of mammalian Wnt proteins may be less dependent on retromer mediated recycling of Wls. The subtle growth defect that we observed could not be fully rescued by supplementation of Wnt3a in the culture medium. Missorting of other retromer cargos such as the CI-MPR, Sortilin or the polarity protein Crumbs, may negatively influence organoid growth. It was recently shown that Lgr5 undergoes retrograde traffic from endosomes to the TGN in Human Embryonic Kidney cells. Therefore, Lgr5 itself may be a retromer cargo in these cells and potentially in the intestinal stem cells. However, the fact that the Vps35?/? organoids were equally dependent on R-Spondin argues against a critical role of retromer in Lgr5 regulation. We were unable to detect endogenous Lgr5 protein in organoid lysates by Western blot, so we could not confirm if Lgr5 is a retromer cargo in intestinal cells. In our experimental approach, we investigated the role of Vps35 in Wnt signaling and stem cell maintenance in intestinal homeostasis of juvenile and adult mice. In these conditions, retromer mediated recycling of Wls is dispensable. There may be situations, for example AbMole Succinylsulfathiazole during embryonic development or during regeneration after injury, which require enhanced levels of Wnt secretion, and may therefore be more dependent on retromer mediated retrograde transport of Wls. For example, Wnt5a signaling is essential for intestinal tube elongation during development and regeneration of the colon after tissue injury. In summary, we show that the retromer complex is required to maintain high Wls protein levels in intestinal epithelial cells, which is in agreement with the current model 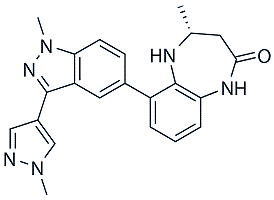 of Wls trafficking. Proliferation and the maintenance of stem cells in organoids are however minimally affected by loss of Vps35. The mouse strain that carries the floxed Vps35 allele will be a valuable tool to study retromer function during development and regeneration of the intestine as well as in other tissues and in different biological contexts. However, there is increasing awareness that myeloid derived immune cells play a significant role in the local tumor microenvironment. In both animal models and cancer patients, for example, myeloid-derived suppressor cells have been implicated in the generation and propagation of local tumor immunosuppression. CAV1 was initially described as a member of a family of scaffolding proteins that interacts with signaling molecules and regulates their activity. It has been reported to have many functions, AbMole Amikacin hydrate including the formation of caveolae, membrane trafficking, signal transduction pathways, apoptosis, calcium and lipid homeostasis in fibroblasts, adipocytes, and endothelial cells.
of Wls trafficking. Proliferation and the maintenance of stem cells in organoids are however minimally affected by loss of Vps35. The mouse strain that carries the floxed Vps35 allele will be a valuable tool to study retromer function during development and regeneration of the intestine as well as in other tissues and in different biological contexts. However, there is increasing awareness that myeloid derived immune cells play a significant role in the local tumor microenvironment. In both animal models and cancer patients, for example, myeloid-derived suppressor cells have been implicated in the generation and propagation of local tumor immunosuppression. CAV1 was initially described as a member of a family of scaffolding proteins that interacts with signaling molecules and regulates their activity. It has been reported to have many functions, AbMole Amikacin hydrate including the formation of caveolae, membrane trafficking, signal transduction pathways, apoptosis, calcium and lipid homeostasis in fibroblasts, adipocytes, and endothelial cells.
Additional methods for modifying drug distribution should be introduced in transcatheter intraarterial therapies
Distance in group tumors probably be the result of the increased pressure difference generated by subsequent embolization of tumor-feeding vessels. An interesting finding was that doxorubicin penetration distance in group 4 tumors was significantly smaller than that in group 3 at 10 minutes but was slightly larger than group 3 at 4 hours. This may be due to the different time intervals AbMole Simetryn between drug delivery and necropsy. Previous experimental studies have shown that Lipiodol, as a carrier of anticancer drugs, can increase intratumoral drug concentration, but that the material mainly retained in microarterioles and venules after intraarterial infusion as a result of its liposolubility. Lewis and colleagues recently performed doxorubicin release experiment in vitro using a T-cell apparatus and found that the drug eluted from doxorubicin/Lipiodol mixture in less than 4 hours, with a half-life of 1 hour. In this study, extracting tumor tissue 10 minutes after treatment will inevitably underestimate the drug penetration in tumors receiving Lipiodol. In contrast, the 4-hour time interval allows doxorubicin to elute from Lipiodol emulsion, leading to the increase in drug penetration. By using fluorescence microscopy, 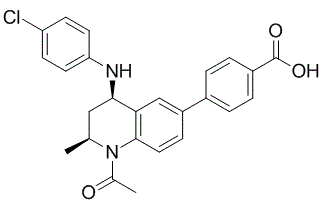 we also showed a significantly increased count of doxorubicin fluorescent spot in three groups of transcatheter therapies compared with vein injection group. It is AbMole Povidone iodine analogous to the findings observed with high performance liquid chromatography in earlier studies, which confirm that transcatheter intraarterial techniques improve drug concentration in liver cancer. Among the three transcatheter intraarterial therapy groups, the change trend of doxorubicin fluorescence count was similar to that of doxorubicin penetration distance, which likely is also explained by the embolization-related drug transportation and Lipiodol-caused drug retention. On the other hand, our study showed that tumor cells in avascular and adjacent regions of tumors receiving transcatheter treatment were not exposed to detectable concentrations of doxorubicin. It is similar to the findings observed in recent studies. Namur and colleagues performed liver transplantation following TACE in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and found that the doxorubicin concentration in tumor tissue decreased with the distance to the occluded vessels and the drug penetration was associated with tumor necrosis. These results suggest that the effect of transcatheter intraarterial techniques currently used on drug distribution could be somewhat limited. Transcatheter intraarterial techniques, because they depend on the existing vasculature, may improve the drug delivery to vascular regions of tumor but fail to improve the delivery to avascular regions.
we also showed a significantly increased count of doxorubicin fluorescent spot in three groups of transcatheter therapies compared with vein injection group. It is AbMole Povidone iodine analogous to the findings observed with high performance liquid chromatography in earlier studies, which confirm that transcatheter intraarterial techniques improve drug concentration in liver cancer. Among the three transcatheter intraarterial therapy groups, the change trend of doxorubicin fluorescence count was similar to that of doxorubicin penetration distance, which likely is also explained by the embolization-related drug transportation and Lipiodol-caused drug retention. On the other hand, our study showed that tumor cells in avascular and adjacent regions of tumors receiving transcatheter treatment were not exposed to detectable concentrations of doxorubicin. It is similar to the findings observed in recent studies. Namur and colleagues performed liver transplantation following TACE in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and found that the doxorubicin concentration in tumor tissue decreased with the distance to the occluded vessels and the drug penetration was associated with tumor necrosis. These results suggest that the effect of transcatheter intraarterial techniques currently used on drug distribution could be somewhat limited. Transcatheter intraarterial techniques, because they depend on the existing vasculature, may improve the drug delivery to vascular regions of tumor but fail to improve the delivery to avascular regions.
CAV1 also suppresses inflammation loss of perfusion in itself does not lead to blood vessel pruning
CAV1 expression has been demonstrated in multiple immune cells including monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes. Similar to our findings in human GBMs, upregulation of CAV1 in murine macrophages dramatically reduced proinflammatory cytokine production and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine production. Reported mechanisms of CAV1 mediated immunosuppression in murine models include inhibition of eNOS activity and activation of the MKK3/p38 pathway. Taken together, these data indicate that GBM-mediated suppression of tumor-associated myeloid cell function is mediated at least in part by CAV1, and importantly, that activity can be restored by suppressing CAV1. Currently FDA approved pharmacological inhibitors of CAV1 such as lovastatin and celecoxib may be useful in AbMole Neosperidin-dihydrochalcone altering the local tumor microenvironment and augmenting current immunotherapy against human glioblastoma and a variety of other solid human tumors characterized by the presence of large numbers of TAMs. The vasculature is the first organ system to form during embryonic development and meets the challenge to grow and refine while it is already functioning. After the initial sprouting of blood vessels, remodeling  ensures the formation of a more efficient vascular network. While many of the key factors and genetic players regulating blood vessel sprouting are known, the mechanisms which control blood vessel remodeling and pruning are only poorly understood. The best-studied context is the regression of the hyaloid vasculature in mice. Here, macrophages secrete a WNT ligand that induces apoptosis in endothelial cells, ultimately leading to the complete removal of this vascular structure. However, in many other contexts where vascular pruning has been described, such as the mouse retina, the branchial arches or the zebrafish brain, only a subset of blood vessel connections is removed. This raises the question: Which mechanism selects the blood vessels to be pruned? In addition, it is unclear how, once a given blood vessel is selected to disconnect and regress, the endothelial cells constituting this previously perfused vessel accomplish to seal it off from the active circulation without causing AbMole Alprostadil hemorrhage. Here, we use time-lapse imaging to analyze the cellular mechanisms that take place during the pruning of a defined blood vessel in the eye of zebrafish embryos. Our analysis reveals that angiogenic sprouting initially leads to the formation of a Yshaped blood vessel branch, which is subsequently resolved. This process entails the rearrangement of endothelial cells within the pruning blood vessel from a multicellular to a partially unicellular tube. We show that blood flow is an important regulator of the pruning event.
ensures the formation of a more efficient vascular network. While many of the key factors and genetic players regulating blood vessel sprouting are known, the mechanisms which control blood vessel remodeling and pruning are only poorly understood. The best-studied context is the regression of the hyaloid vasculature in mice. Here, macrophages secrete a WNT ligand that induces apoptosis in endothelial cells, ultimately leading to the complete removal of this vascular structure. However, in many other contexts where vascular pruning has been described, such as the mouse retina, the branchial arches or the zebrafish brain, only a subset of blood vessel connections is removed. This raises the question: Which mechanism selects the blood vessels to be pruned? In addition, it is unclear how, once a given blood vessel is selected to disconnect and regress, the endothelial cells constituting this previously perfused vessel accomplish to seal it off from the active circulation without causing AbMole Alprostadil hemorrhage. Here, we use time-lapse imaging to analyze the cellular mechanisms that take place during the pruning of a defined blood vessel in the eye of zebrafish embryos. Our analysis reveals that angiogenic sprouting initially leads to the formation of a Yshaped blood vessel branch, which is subsequently resolved. This process entails the rearrangement of endothelial cells within the pruning blood vessel from a multicellular to a partially unicellular tube. We show that blood flow is an important regulator of the pruning event.