We found weak positive association between CETP and PLTP activities and mean particle diameter of HDL and other variables related to extra-large HDL particles at baseline. Overall, CETP can be seen as one among the factors affecting reverse cholesterol transport pathway and high CETP activity is reportedly associated with decreased HDL cholesterol levels. CETP inhibitors have recently gained great interest due to their ability to increase HDL cholesterol concentration, but it remains to be seen whether their use will result in functionally protective HDL populations and clinical benefit in large trials. Although the effects of intervention on clinical characteristics and measured 20S-Notoginsenoside-R2 metabolites were modest, we found a strong association between increased fish intake and variables related to large HDL particles. However, as a potential limitation, our study design does not allow for total separation of fish intake from increased intake of whole grain and low insulin response grain products and bilberries, but this was considered in statistical analyses by including the intervention group into the model. In fact, not all subjects in the third tertile with the greatest increase in fish intake were in the HealthyDiet group. The average consumption of fish was 74 grams per day in the third tertile, which is more than 500 g per week. This suggests that the instructed three fish meals per week were not enough for these changes. The mean consumption of fish in the third tertile was more than double of average fish consumption among the Finnish population. We have seen that people who are willing to participate in dietary interventions are more interested in healthy eating than people in average. This phenomenon is also observed when comparing the baseline nutrient intakes in the 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol present study with the respective average intakes in Finland. This is one obvious explanation why it might be difficult to see significant changes in the intervention groups with healthy diet. For the same reason, people in the Control group had to limit their rye bread, fish and berry intake, so that the control diet resembled more an average Finnish diet. For example, rye bread intake in men in the Northern Savo area is more than double compared to corresponding intake in Southern Finland. Besides lipoprotein subclass distribution and detailed information on serum lipids, the NMR platform enables detection of lowmolecular-weight metabolites including e.g. citrate, acetate, urea and amino acids. We did not see changes in these 22 measured metabolites during the intervention. The battery of 22 lowmolecular-weight metabolites was not selected particularly for this dietary intervention study and we did not have preliminary hypothesis related to these metabolites. Furthermore, the power calculation was based on fasting glucose concentration, and it is possible that there was not enough power to see all changes in these secondary outcome variables. Of these metabolites, branched chain amino acids were probably the most interesting ones, because they are related to type 2 diabetes risk and we have earlier found that serum isoleucine decreased after the 12 week consumption of diet high in rye bread and pasta. Despite similar carbohydrate modification of 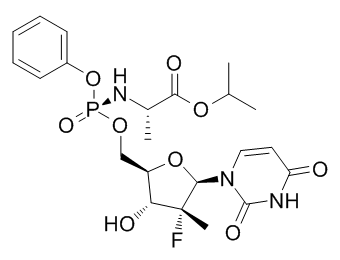 the diet in the HealthyDiet and WGED groups of the present study, we could not see any changes in isoleucine. This confirms our earlier conclusion that decreased isoleucine may rather be due to decreased intake of protein rich foods.
the diet in the HealthyDiet and WGED groups of the present study, we could not see any changes in isoleucine. This confirms our earlier conclusion that decreased isoleucine may rather be due to decreased intake of protein rich foods.
Month: May 2019
The patterns of CIN detected in canine mammary tumors were similar to the types of rearrangements
Supplements against overall cardiovascular events among patients with a history of cardiovascular disease. The effect on glucose and insulin metabolism has been inconsistent, but possible adverse effects on glucose metabolism related to especially higher doses may be compensated by improved serum triglyceride concentration in diabetic subjects.The results of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis lend support to the biological significance of gene expression profiles derived from the deep sequencing, which will assist in the discovery and annotation of P. capsici genes playing key roles in development and particularly in pre-infection stages. It is not surprising that the ribosome-related’pathways were the most Tubeimoside-I affected for the DEGs more common in ZO and GC libraries. This finding implies that the oomycete utilizes new ribosomes or changes in ribosome components to help synthesize additional proteins to facilitate its swimming towards potential host plants and subsequent germination on host surface. Sequencing of plant pathogenic oomycetes has revealed a variable number of effectors in different species. In the present study, 99 P. capsici effector genes were identified with known or putative roles in virulence. We predicted that these RXLRs, CRNs, NLPs and elicitins would be highly expressed during pre-infection and infection stages.We elected to only remove half the culture medium every other day until day five so that the hostparasite interface remained Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate undisturbed until the infection was established. After five days, parasite density peaked and Pancuronium dibromide unattached parasites had to be removed daily. This approach mimics in vivo conditions where unattached parasites are pushed down the intestine and are ultimately excreted from the host. Although the 90/10 media mix does not support trophozoite survival in the absence of Caco-2 cells in plate cultures, we have shown inserts provide a more suitable environment for trophozoite proliferation. Therefore, further optimization of the insert model, such as altering parasite inoculation density or media composition, could allow parasite survival in the absence of host cells. This would make assessment of host-induced changes in Giardia gene expression feasible using our developed model. Our experimental design recapitulates the architecture of the gastrointestinal tract where Giardia trophozoites attach apically to the epithelium and epithelial cells interact basolaterally with macrophages in the lamina propria. Using human differentiated macrophages isolated from buffy coats for the cytokine array further illustrates the versatility of the model. However, due to low isolation numbers, lack of proliferation, and difficulty in maintaining the human monocyte-derived macrophages in culture, IC-21 cells were used in all other experiments to characterize our model. Epithelial cell apoptosis as a mechanism of barrier dysfunction during giardiasis has been well documented in vitro, in human biopsies, and in mouse models with G. muris. However, the results of those experiments have been contradictory with regards to the degree of apoptosis observed as well as the Giardia assemblage capable of inducing epithelial cell death. Studies using sonicated Giardia lamblia strain WBC6, failed to elicit epithelial cell apoptosis ; a finding inconsistent with other work using live WBC6 trophozoites.
This is consistent with earlier findings of increases in large HDL particles and decreases of small particles
Quantitative dependent variables were transformed to base-10 logarithmic scale to account for non-normal distributions. Selected confounding phenotypes was used to examine group related changes during the intervention. Control group was used as a reference group when comparing group differences. Benjamini�CHochberg false discovery rate was used to adjust the metabolomics measures and dietary intake results for multiple comparisons. Adjustment was done by one treatment effect at a time and in clinically relevant sets. FDRadjusted p-value # 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. All these analyses are secondary though aimed to be done in the original study protocol. The primary aim of the study was to examine effects on glucose metabolism. Associations between the changes in fish intake and changes in variables related to large HDL particles were tested using analyses of covariance. Intervention group, age, gender, BMI and fasting glucose were included into models. Analyses were performed using standardized variables. Differences between the fish intake tertiles were tested using one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc comparisons. Baseline associations were studied applying linear regression model including age, gender, BMI and fasting glucose into models. In the present study the effects of diets containing fatty fish, wholegrain and low insulin response grain products, and bilberries on clinical characteristics, serum metabolites and lipid transfer Gambogic-acid protein activities in persons with impaired glucose metabolism were investigated. We found significant changes in lipid metabolites in the HealthyDiet group reflecting increased polyunsaturation of plasma fatty acids, particularly increase in n-3 PUFAs. Atropine sulfate Furthermore, in the within-the-group comparisons we found an increasing trend in variables related to large HDL particles in the HealthyDiet group, and when analysing this in more detail we found that the increase of fish intake correlated strongly 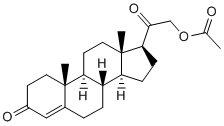 with the increased concentration of large HDL particles, larger average diameter of HDL particles and increased concentrations of large HDL lipid components. Significant changes in lipid metabolites in the HealthyDiet group were observed. All changes reflected increased polyunsaturation in plasma fatty acids, especially increase in n-3 PUFAs, while n-6 and n-7 fatty acids decreased. This is consistent with our earlier findings of increased plasma content of long chain polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids and increase of plasma Tg incorporating the long chain PUFA in the HealthyDiet group. These findings also confirm that different analytical methods, give consistent results for comparable lipid measures. The observed changes confirm the good compliance to the instructions of fish intake, since the subjects in the HealthyDiet group were advised to eat fatty fish at least three times per week, whereas subjects in the Control group where instructed to restrict their fish intake for maximum of 1 fish meal per week. In the WGED group, dietary habits, besides the cereal products, were advised to keep unchanged, which did not cause changes in the measured metabolites. Serum total, LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, serum Tg or serum apoA-1 and apoB100 concentrations did not change during the intervention. We observed that a greater increase of fish intake was associated with increased concentration of large HDL particles, larger average diameter of HDL particles and increased concentrations of lipid components in large HDL particles.
with the increased concentration of large HDL particles, larger average diameter of HDL particles and increased concentrations of large HDL lipid components. Significant changes in lipid metabolites in the HealthyDiet group were observed. All changes reflected increased polyunsaturation in plasma fatty acids, especially increase in n-3 PUFAs, while n-6 and n-7 fatty acids decreased. This is consistent with our earlier findings of increased plasma content of long chain polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids and increase of plasma Tg incorporating the long chain PUFA in the HealthyDiet group. These findings also confirm that different analytical methods, give consistent results for comparable lipid measures. The observed changes confirm the good compliance to the instructions of fish intake, since the subjects in the HealthyDiet group were advised to eat fatty fish at least three times per week, whereas subjects in the Control group where instructed to restrict their fish intake for maximum of 1 fish meal per week. In the WGED group, dietary habits, besides the cereal products, were advised to keep unchanged, which did not cause changes in the measured metabolites. Serum total, LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, serum Tg or serum apoA-1 and apoB100 concentrations did not change during the intervention. We observed that a greater increase of fish intake was associated with increased concentration of large HDL particles, larger average diameter of HDL particles and increased concentrations of lipid components in large HDL particles.
The NLR and PLR have been reported to be important prognostic models with a variety of solid cancers
Several studies have also shown that an elevated NLR is associated with poor prognosis in patients with NPC. In accord with the study of Jian-rong He et al. who tested the prognostic value of NLR in 1410 patients with various stages of NPC and the study of Xin An et al. who tested the prognostic value of NLR in 363 patients with non-disseminated NPC, we also found a significant association between NLR and OS. However, the COX model and the AUC analysis have shown that the GPS was superior to NLR in terms of discriminating ability and prognostic accuracy. For PLR, it was not independently associated with overall survival. In general, this study is the first to show the superior prognostic ability of the GPS over the NLR and PLR in patients with metastatic NPC. In conclusion, our study demonstrated that the GPS may be useful to predict the prognosis of metastatic NPC patients Estradiol Benzoate treated with cisplatin-based palliative chemotherapy and facilitate individualized treatment. A prospective study to validate this prognostic model is needed. The mechanisms underlying the relationship between high GPS and poor prognosis in NPC still need further study. The leather industry is one of the oldest industries in the world, which nowadays plays a large role in the economic system worldwide. Looking through the ages, we can state that leather is a sustainable material, because while people eat meat, they will have this raw material available. Despite incomes, the leather industry is a high pollutant industry. The reason for this is that leather is not a ”friend” of the environment, as it plays a role in the environmental destruction caused by the meat industry as well as the pollution caused by the materials used in leather preservation and processing. For this reason, raw hide preservation has always been a challenge for leather manufacturers. The raw hides and skins are flayed from the animal and further processed into leather. As the main constituent of raw skins and hides is protein, these materials are highly susceptible to bacterial action. Deterioration of the skin starts within 5�C6 h after flaying; hence, there is a requirement for an effective preservative. Thus, it is essential to preserve the protein matrix and also to temporarily arrest microbial attacks. The preservation of raw stock has the objective of rendering the flayed skin/hide resistant to putrefaction in order to allow transport and storage. Preservation is accomplished either by destroying active bacteria, by preventing bacterial activity or by preventing bacterial contamination. During preservation, it is essential to avoid the use of toxic materials, as these are very dangerous for the environment due to their chemical nature. From ancient times, common salt and its sub-empirical forms like Khari salts have been employed for preservation. These salts are available to flayers and slaughterhouses globally. Preservation using salt remains the most popular curing technique worldwide due to its ease, cost-effectiveness and the quality of the finished leather produced. The use of salt enhances the pollution load of tannery effluent, however, which becomes highly contaminated with increased  total dissolved solids and chlorides. To overcome this hurdle, researchers are constantly searching for alternative preservation techniques which are either totally void of salt or use only a small amount. Sundar and Muralidharan developed a low Alprostadil salt-MgO substituted skin preservation methodology. The methodology bases the amount of salt required on the weight of the skin to be treated, and uses less than 25% of the weight of the skin.
total dissolved solids and chlorides. To overcome this hurdle, researchers are constantly searching for alternative preservation techniques which are either totally void of salt or use only a small amount. Sundar and Muralidharan developed a low Alprostadil salt-MgO substituted skin preservation methodology. The methodology bases the amount of salt required on the weight of the skin to be treated, and uses less than 25% of the weight of the skin.
The solution by iodometric titration to an increase of the temperatures of the first endothermic effect
Strength properties, the amount of chrome compounds in leather, soluble matter in dichloromethane, and volatile matter were determined according to standards. Shrinkage temperature of chromed leather samples was determined as described in the literature using special equipment and replacing the distilled water with glycerol. The next step was to discover how the action of microorganisms affects derma collagen. The index, which is very sensitive to collagen structural changes, is the shrinkage temperature of hide. The results of hide shrinkage temperature determination did not show any serious changes in derma structure. For all samples, only a negligible decrease of shrinkage temperature was observed. This indicates that the action of microorganisms, which takes place only on the surface of the hide, does not affect the deeper layers of the hide. This remains true even when bacteria act in a very intensive manner. Therefore, it can be concluded that changes in shrinkage temperature do not reflects a level of hide deterioration when no chemical material is used for hide preservation, and collagen, accordingly, is not affected by this material. Another index which indicates a condition of preserved hide is the amount of ammonia released, which is formed when the hydrolysis of proteins begins due to the action of microorganisms. The data in Table 3 show that the 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol observable increase of the amount of extracted nitrogen begins only for unpreserved hide after 13 days of storage. This result confirms a proposition that hide can be stored at 4uC for 2 weeks without compromising its quality. In the case of vacuumed and salted hide samples, the increment of nitrogen content was negligible. One of initial symptoms of deterioration is a change to the exterior of the hide. As a result, a Diperodon comparison of the hide samples was carried out. The optical microscopy images are presented in Fig. 3. The exploration of images allowed the conclusion to be drawn that any observable changes to the outside and inside of the hide did not occur during the 22 day storage period. Furthermore, possible changes of the supermolecular structure during storage under vacuum were investigated. FTIR spectroscopy and DSC analysis were carried out for this purpose. The structural changes reflect in the FTIR spectra as changes of individual bands in both position and intensity. A comparison of the peak area values allows a conclusion to be drawn about the formation of functional groups and the degradation or formation of bonds during hide storage. The most typical bands in the spectra were chosen for evaluation of structural changes. From studying the spectra of the hide samples it can be seen that no novel peaks were identified, and there was no loss of existing peaks. This indicated that any serious changes in supermolecular structure of collagen do not occur during the 22 day storage period. On the other hand, the intensity of all peaks was found to increase. The authors hypothesise that, owing to the action of vacuum during storage, the collagen fibres slowly become closer, making the derma becomes denser, which leads to the increased peak intensity in spectra from the hide samples that were stored for 22 days. The results of DSC analysis are presented in Fig. 5 and Table 5. It  can be seen that DSC curves have three distinct thermal effects. The first endothermic effect can be attributed to shrinkage of the hide. However, a more credible suggestion is the association of that effect with the removal of capillary moisture. It is known that the degree of linking of capillary moisture in collagen is higher when capillaries are smaller. Presumably, the closer proximity of fibres during storage under vacuum leads to a decrease of capillary dimensions, and accordingly.
can be seen that DSC curves have three distinct thermal effects. The first endothermic effect can be attributed to shrinkage of the hide. However, a more credible suggestion is the association of that effect with the removal of capillary moisture. It is known that the degree of linking of capillary moisture in collagen is higher when capillaries are smaller. Presumably, the closer proximity of fibres during storage under vacuum leads to a decrease of capillary dimensions, and accordingly.