As the MARS 500 volunteers had no cardiovascular or other pathology, or risk factors when entering the 10-Gingerol confinement habitat it is difficult to suggest a pathological mechanism for explaining the IMT increase. Moreover the diameter of the arteries concerned did not change at all. Thus we suggest that the increase in IMT should be related to one or several environmental factors of the confinement habitat. There was no change in gravity, atmospheric pressure, oxygen pressure, and slight changes in nutrition or physical activity�� compared to sedentary people not living in a confined environment. One may suggest that other factors like the isolation from the outside, the supposed outside risky environment itself, the absence of solar radiation could request an adaptation of some of the human body function and trigger metabolic processes. An oxidative 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C stress related to confinement could be a factor involved into the vascular changes observed during MARS 500. Oxidative stress is related to abnormal oxygen metabolism which produces nitric oxide and other element known to favor inflammatory reaction at the vascular level with increased IMT. Such hypothesis is supported by the results from a 105 d confinement experiment performed one year ago in the same facility as for MARS 500. This study reported an increase in oxidative stress with increase in oxi-hemoglobin, and decrease in some antioxidant defense. Other studies reported that confinement induce mental and physical stress that were found to disturb several cardiovascular target properties like arterial stiffness, endothelium properties, capillary permeability in relation with edema, or homodynamic parameters, or parameters regulating cardiovascular status like autonomous nervous system, insulin resistance, increase cathecholamines, angiotensine II, nitric oxide. In normal population longitudinal studies showed that social isolation in children was associated with higher cardiovascular risk factors when adults, and that social isolation in adult also increased cardiovascular risk factors. Depression, anxiety, mental disorder that can be induced by confinement are also considered as cardiovascular risk factors. Confinement was also found to reduce capacity to concentrate and increase the time needed to make a decision. Thus putting together several individuals of various personality may create tension or collaborative influence between the participant and generate mental stress. Coronary ectasia is an uncommon disease and its incidence has been reported as between 0.3 and 5% in different studies despite some exception. It is defined as the diameter of the ectatic segment being more than 1.5 times larger compared with an adjacent healthy reference segment. Most cases of CE are considered as a variant  of coronary artery disease. The pathogenesis of CE is not completely illustrated. However, it is likely to involve the destruction of the arterial media, increased wall stress, thinning of the arterial wall, and progressive dilatation of the coronary artery segment. The development of coronary collaterals is an adaptive response to chronic myoischemia and serves as a conduit bridging the significantly stenotic coronary vessels. Collateral circulation can hence protect and preserve myocardium from episodes of ischemia, enhance residual myocardial contractility, and reduce angina symptoms and cardiovascular events. However, there is inter-individual difference of coronary collateral formation and the mechanisms for the different individual ability to develop collateral circulation are still unclear. Because CE are usually associated with atherosclerosis and even obstructive CAD resulting coronary ischemia, whether the presence of good coronary collateral or not is a very important issue.
of coronary artery disease. The pathogenesis of CE is not completely illustrated. However, it is likely to involve the destruction of the arterial media, increased wall stress, thinning of the arterial wall, and progressive dilatation of the coronary artery segment. The development of coronary collaterals is an adaptive response to chronic myoischemia and serves as a conduit bridging the significantly stenotic coronary vessels. Collateral circulation can hence protect and preserve myocardium from episodes of ischemia, enhance residual myocardial contractility, and reduce angina symptoms and cardiovascular events. However, there is inter-individual difference of coronary collateral formation and the mechanisms for the different individual ability to develop collateral circulation are still unclear. Because CE are usually associated with atherosclerosis and even obstructive CAD resulting coronary ischemia, whether the presence of good coronary collateral or not is a very important issue.
Category: MAPK Inhibitor Library
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of menthol in an ethanol-induced gastric ulcer model were investigated
The dose of menthol used in this study was selected based on previous results reported by our group showing the gastroprotective effect of menthol. It was observed that treatment with menthol provided 92% gastroprotection compared to treatment with a vehicle control; this level of gastroprotection that is similar to the effect of the standard drug carbenoxolone. The mechanisms responsible for the gastroprotective effect were also investigated. HSPs are a type of protective protein involved in diverse biological activities, including apoptosis. Gomisin-D HSP-70 is a molecular chaperone that is rapidly induced by stresses such as heat, oxidative stress, and drug exposure. Therefore, drugs or treatments that induce HSP-70 expression may positively contribute to gastric mucosal defense and cytoprotection. In addition to its cytoprotective effect, HSP-70 has anti-apoptotic activity and can decrease oxidative stress and cell injury. The induction of HSP-70 is part of the gastroprotective mechanism of menthol. Furthermore, the inhibition of apoptosis in the gastric mucosa of rats treated with menthol can be partially explained by menthol’s HSP-70-inducing effect. It has been suggested that an interaction between the expression of the HSP-70 and the proapoptotic Bax genes may occur under stress conditions, with suppression of Bax activation in cells with high HSP-70 levels. There is growing evidence that ethanol administration promotes oxidative stress by increasing the Tetrahydroberberine formation of ROS and depleting cellular oxidative defenses in a process triggered by neutrophil activation, causing a sequential ROS-mediated induction of lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation. Recent studies have linked the genesis of ethanol-induced gastric ulcers to the number of infiltrated neutrophils. The MPO is the main marker of neutrophil infiltration in ulcerogenic lesions. This enzyme is found within the neutrophils and catalyzes the oxidation of the chloride ion by hydrogen peroxide to form hypochlorous acid, which is toxic to pathogenic microorganisms but is also harmful to host tissues. This process is responsible for the generation of free radicals, resulting in an acute inflammation in the gastric tissue. The gastroprotection induced by menthol can be partially explained by the inhibition of neutrophil infiltration and subsequent MPO generation. Neutrophils also produce the superoxide radical anion, the product of the reaction of oxygen molecules and electrons from the transport chain in mitochondria. The cells of the gastrointestinal tract have an antioxidant defense system  that is capable of preventing the cytotoxicity of ROS through mechanisms that involve the action of enzymes and compounds with the potential to scavenge free radicals and prevent their destructive action. The major antioxidative enzyme is SOD, which catalyzes the dismutation of O22 into less noxious H2O2, which is further degraded by catalase or GSH-Px. The activity of SOD was decreased in the stomachs of mentholor carbenoxolone-treated rats. We propose that this is an interesting finding because the relatively higher SOD activity in vehicle-treated rats indicates a greater production of O22. The increases in the amounts of the GSH-Px and GR enzymes and the antioxidant compound glutathione, associated with the inhibition of MPO production, confirm the antioxidant activity of the menthol in gastric ulcers and support an important role for oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of ethanol-induced gastric ulcers. There are several reports in the literature indicating that the administration of potential antioxidant natural products can prevent the gastric damage caused by the action of ethanol.
that is capable of preventing the cytotoxicity of ROS through mechanisms that involve the action of enzymes and compounds with the potential to scavenge free radicals and prevent their destructive action. The major antioxidative enzyme is SOD, which catalyzes the dismutation of O22 into less noxious H2O2, which is further degraded by catalase or GSH-Px. The activity of SOD was decreased in the stomachs of mentholor carbenoxolone-treated rats. We propose that this is an interesting finding because the relatively higher SOD activity in vehicle-treated rats indicates a greater production of O22. The increases in the amounts of the GSH-Px and GR enzymes and the antioxidant compound glutathione, associated with the inhibition of MPO production, confirm the antioxidant activity of the menthol in gastric ulcers and support an important role for oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of ethanol-induced gastric ulcers. There are several reports in the literature indicating that the administration of potential antioxidant natural products can prevent the gastric damage caused by the action of ethanol.
The only approved therapy for acute thromboembolic stroke remains to improve glucose
SlimFast and Glucerna have been used by participants of the Look AHEAD study but only as part of other sources of nutrient intake and of unknown mechanistic actions. Our experiments showed that all popular meal replacement drinks, along with AbMole Diatrizoic acid non-fat milk, had a stimulatory effect on FGF19. AbMole Miglitol Ensure Clear had the most potent effect and it should be noted that it was the only drink that did not contain any form of fat which is similar to non-fat milk which also had a potent stimulatory effect on FGF19 mRNA. We hypothesize that the absence of fat in these two drinks, and/or the presence of a yet-tobe determined ingredient may be responsible for the enhanced potency of the effect in Ensure clear and non-fat milk on FGF19 expression. Further experiments using individual components would need to be performed to address this question. Caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee in particular, also had potent stimulatory effects on FGF19 expression. Using two different concentrations of caffeine, we showed that caffeine itself is unlikely to be the stimulatory ingredient. In fact, the 10-fold higher concentration of caffeine significantly attenuated FGF19 expression. It would therefore appear that the stimulatory effects of coffee are due to other ingredients in the coffee beans that, in vivo, have been shown to stimulate incretins. Consumption of coffee, and in particular decaffeinated coffee have been consistently associated with reduced risk for developing type 2 diabetes. The analogous effects of decaffeinated coffee on the stimulation of FGF19 and its reported association with reduced risk of diabetes could potentially be correlated. It would therefore be of interest to measure in the future FGF19 levels in humans consuming 4�C8 cups of decaffeinated coffee and compare them to participants who are not  consuming coffee. The 5-hour energy drink was the only liquid that downregulated FGF19 mRNA. This could be due to the potential presence of stimulants like caffeine which are not specified on the label of the product, or other components like niacin, vitamin B6, or folic acid that are listed on the label. In summary, meal replacement drinks, non-fat milk, and coffee had powerful stimulatory effects on FGF19 expression. This could potentially be beneficial in reducing risk for diabetes development because higher FGF19 levels are associated with non-diabetes and diabetes remission after RYGB surgery. High caffeine concentration and the 5-hour energy drink, on the other hand, had negative effects on FGF19 expression. These data should be corroborated by in vivo studies before any conclusions can be made regarding the beneficial effects of these popular drinks towards FGF19 expression and their potential effects with respect to the development of diabetes in humans. Sudden occlusion of a cerebral blood vessel by a thrombus or embolism initiates a complex process of events that includes excitotoxity, oxidative stress, microvascular injury, blood brain barrier dysfunction and postischemic inflammation that ultimately leads to cell death. Although several mechanisms are involved in the pathophysiology of stroke, increasing evidence shows that inflammation is a key contributor to the pathophysiology of cerebrovascular diseases and this correlates with the outcome of the patient. Inflammation contributes to breakdown of the blood-brain barrier which promotes the formation of brain edema and contributes to acute mortality in stroke. In the acute phase of stroke activation of cytokines, chemokines, matrix metalloproteinases, adhesion molecules ICAM-1, Pselectin, E-electin and toxic molecules such as nitric oxide, free radicals, apoptosis, and stress genes occurs.
consuming coffee. The 5-hour energy drink was the only liquid that downregulated FGF19 mRNA. This could be due to the potential presence of stimulants like caffeine which are not specified on the label of the product, or other components like niacin, vitamin B6, or folic acid that are listed on the label. In summary, meal replacement drinks, non-fat milk, and coffee had powerful stimulatory effects on FGF19 expression. This could potentially be beneficial in reducing risk for diabetes development because higher FGF19 levels are associated with non-diabetes and diabetes remission after RYGB surgery. High caffeine concentration and the 5-hour energy drink, on the other hand, had negative effects on FGF19 expression. These data should be corroborated by in vivo studies before any conclusions can be made regarding the beneficial effects of these popular drinks towards FGF19 expression and their potential effects with respect to the development of diabetes in humans. Sudden occlusion of a cerebral blood vessel by a thrombus or embolism initiates a complex process of events that includes excitotoxity, oxidative stress, microvascular injury, blood brain barrier dysfunction and postischemic inflammation that ultimately leads to cell death. Although several mechanisms are involved in the pathophysiology of stroke, increasing evidence shows that inflammation is a key contributor to the pathophysiology of cerebrovascular diseases and this correlates with the outcome of the patient. Inflammation contributes to breakdown of the blood-brain barrier which promotes the formation of brain edema and contributes to acute mortality in stroke. In the acute phase of stroke activation of cytokines, chemokines, matrix metalloproteinases, adhesion molecules ICAM-1, Pselectin, E-electin and toxic molecules such as nitric oxide, free radicals, apoptosis, and stress genes occurs.
ET-1 plays a central role in differences in blood flow between vessels in a branch point
The knowledge of genes and pathways involved in disease is of great importance to understand the pathogenic mechanisms of disease, and consequently to improve therapy, diagnosis and disease prevention. Linkage and association studies in human are commonly used to identify candidate susceptibility loci in Mendelian disorder. However, the heterogeneity of the human genome, the minor single gene contribution to the pathogenesis, and the multiplex gene-gene and gene-environment interactions render challenging to identify genes with low effect in complex disease. Therefore, animal models are invaluable tools to decipher genetic factors affecting quantitative traits, since they allow us to control the genetic background and to define the environmental conditions. It is highly toxic  to humans and is associated with high mortality, mainly as a consequence of respiratory failure. The most common poisoning route is by ingestion of the concentrated solution, either intentional or accidental. On rare occasions, there are also cases of intoxication by way of dermal exposure or intravenous AbMole 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid injections. Dermal exposure reportedly results in severe PQ poisoning, especially in the presence of pre-existing skin lesions. Intravenous PQ poisoning is rare, and the clinical presentation and prognosis of such a scenario would be quite different from that of oral ingestion. Plasma PQ levels peak at two hr after PQ ingestion and decrease rapidly. PQ is eliminated by the kidney in urine. Severe PQ poisoning is characterized by multiple-organ failure, which mainly involves the lungs, kidneys, liver, heart and also the nervous system. The lung is a major target organ in paraquat poisoning, and respiratory failure from lung injury is the most common cause of death. The exact mechanism of PQ poisoning is currently unknown. Because of a lack of effective antidotes, conventional supportive treatments are poor and have a high mortality rate. Many scholars are devoted to this subject. Pulse AbMole Capromorelin tartrate therapy with cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone has significantly prevented pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Endothelin is an endothelium-derived 21-residue vasoconstrictor peptide. It was isolated by a Japanese scholar in 1988, and has been shown to be one of the most potent known vasoconstrictors. The ETs have three distinct isoforms, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo, and it is the only one that is constitutively released by the vascular endothelium. In addition, ET-1 is also produced by smooth muscle cells, macrophages, airway epithelium, and alveolar epithelial cells. ET-1 is released following various injurious stimuli, including shear stress, thrombin, angiotensin II, cytokines, and free radicals.
to humans and is associated with high mortality, mainly as a consequence of respiratory failure. The most common poisoning route is by ingestion of the concentrated solution, either intentional or accidental. On rare occasions, there are also cases of intoxication by way of dermal exposure or intravenous AbMole 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid injections. Dermal exposure reportedly results in severe PQ poisoning, especially in the presence of pre-existing skin lesions. Intravenous PQ poisoning is rare, and the clinical presentation and prognosis of such a scenario would be quite different from that of oral ingestion. Plasma PQ levels peak at two hr after PQ ingestion and decrease rapidly. PQ is eliminated by the kidney in urine. Severe PQ poisoning is characterized by multiple-organ failure, which mainly involves the lungs, kidneys, liver, heart and also the nervous system. The lung is a major target organ in paraquat poisoning, and respiratory failure from lung injury is the most common cause of death. The exact mechanism of PQ poisoning is currently unknown. Because of a lack of effective antidotes, conventional supportive treatments are poor and have a high mortality rate. Many scholars are devoted to this subject. Pulse AbMole Capromorelin tartrate therapy with cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone has significantly prevented pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Endothelin is an endothelium-derived 21-residue vasoconstrictor peptide. It was isolated by a Japanese scholar in 1988, and has been shown to be one of the most potent known vasoconstrictors. The ETs have three distinct isoforms, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo, and it is the only one that is constitutively released by the vascular endothelium. In addition, ET-1 is also produced by smooth muscle cells, macrophages, airway epithelium, and alveolar epithelial cells. ET-1 is released following various injurious stimuli, including shear stress, thrombin, angiotensin II, cytokines, and free radicals.
Bosentan therapy has shown to increase susceptibility to infection no symptoms of infection were observed
Differentiation, contraction, and AbMole Ellipticine collagen synthesis. It also independently 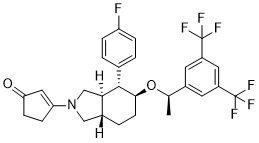 promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The plasma ET levels in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than those of the AbMole Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate controls. Bosentan is a dual endothelin-receptor antagonist that can be taken orally, and in patients with severe PH, it can improve exercise capacity, hemodynamics and quality of life. Bosentan application to bleomycin-treated rats resulted in significantly higher exercise capacity as a result of improvements in PH and PF and improvements in their quality of life. The present data suggests a therapeutic utility for bosentan, particularly in treating the early stages of chronic inflammatory airway diseases. The present study was designed to evaluate the effects of bosentan as a PQ poisoning treatment. Over the past few years, cytokine research has brought new ideas to PQ therapy. TGF-b1 is a multifunction cytokine; it can stimulate the proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, synthesize extracellular matrix and suppress collagen degradation, promote collagen deposition, and it may then play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of PF. One domestic study found that the level of caveolin-1 decreased in rats after PQ exposure. Caveolin-1 notably downregulates transforming growth factor-b signal transduction by modulating TGF-b1 receptor gene expression, preventing Smad2 phosphorylation, and/or mediating TGF-b receptor turnover. ET-1 also plays a central role in lung fibrosis. ET-1 has been shown to induce fibroblast proliferation, differentiation, contraction, and collagen synthesis. It also independently promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The levels of plasma ET in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than in the controls. An ETA receptor antagonist was shown to inhibit the development of paraquat-induced PF, confirming the importance of ET-1 in mediating PF in a rat experiment. There are three distinct isoforms endothelins, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3 and two endothelin receptors, namely ETA-R and ETB-R. ETA-R mainly resides in smooth muscle cells, and ETB-R is in the endotheliocyte. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo one of the two receptors. Bosentan is a nonselective dual endothelin-receptor antagonist, and it is widely used to treat PH. It can improve the exercise capacity and hemodynamics of PH patients. In recent years, bosentan has been shown to have some function in acute lung injury and PF by three methods, which included reducing the right ventricular systolic pressure, decreasing reactive oxygen species release and relieving the inflammatory reaction.
promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The plasma ET levels in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than those of the AbMole Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate controls. Bosentan is a dual endothelin-receptor antagonist that can be taken orally, and in patients with severe PH, it can improve exercise capacity, hemodynamics and quality of life. Bosentan application to bleomycin-treated rats resulted in significantly higher exercise capacity as a result of improvements in PH and PF and improvements in their quality of life. The present data suggests a therapeutic utility for bosentan, particularly in treating the early stages of chronic inflammatory airway diseases. The present study was designed to evaluate the effects of bosentan as a PQ poisoning treatment. Over the past few years, cytokine research has brought new ideas to PQ therapy. TGF-b1 is a multifunction cytokine; it can stimulate the proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, synthesize extracellular matrix and suppress collagen degradation, promote collagen deposition, and it may then play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of PF. One domestic study found that the level of caveolin-1 decreased in rats after PQ exposure. Caveolin-1 notably downregulates transforming growth factor-b signal transduction by modulating TGF-b1 receptor gene expression, preventing Smad2 phosphorylation, and/or mediating TGF-b receptor turnover. ET-1 also plays a central role in lung fibrosis. ET-1 has been shown to induce fibroblast proliferation, differentiation, contraction, and collagen synthesis. It also independently promotes fibroblast resistance to apoptosis through signaling pathways. The levels of plasma ET in patients with MODS caused by acute PQ poisoning were much higher than in the controls. An ETA receptor antagonist was shown to inhibit the development of paraquat-induced PF, confirming the importance of ET-1 in mediating PF in a rat experiment. There are three distinct isoforms endothelins, namely ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3 and two endothelin receptors, namely ETA-R and ETB-R. ETA-R mainly resides in smooth muscle cells, and ETB-R is in the endotheliocyte. ET-1 is the most abundant isoform and the best characterized in vivo one of the two receptors. Bosentan is a nonselective dual endothelin-receptor antagonist, and it is widely used to treat PH. It can improve the exercise capacity and hemodynamics of PH patients. In recent years, bosentan has been shown to have some function in acute lung injury and PF by three methods, which included reducing the right ventricular systolic pressure, decreasing reactive oxygen species release and relieving the inflammatory reaction.