This was considered important knowing the homing characteristics of pDC to the T-cell area in the activated lymph nodes. Interestingly, both IFN-c the major Th1 and IL-4 the major Th2 cytokine promoted pDC activation and survival. This indicates that the Th1/Th2 system does not imprint a particular bias on pDC but rather AbMole Seratrodast supports their function during a T-cell response. Nevertheless, it should be noted that porcine IL4 has been reported to functionally differ from human and mouse IL-4 at least with respect to its ability to promote B-cell activation and this author has questioned the role of IL-4 in the porcine Th1Th2 paradigm. Furthermore, IL-4 has been difficult to detect, both at the protein and mRNA level, in vitro and in vivo. It is possible that in particular breeds of pigs IL-13 could have a more prominent role for porcine Th2 responses. On the other hand, both IL-4 and IL-13 are able to induce the generation of monocytes-derived DC in the pig and to prevent apoptosis of endothelial cells. Independent of this issue requiring further clarification, pDC are more likely to promote Th1 responses through secretion of type I IFNs, IL-12 and TNF-a. We and others have also found this profile of cytokines for porcine pDC. As expected from studies with other species, the antiinflammatory cytokine IL-10 represents a main negative regulator of porcine pDC. This cytokine is produced by regulatory T cells, and many other cells such as monocytes/macrophages, B cells and DC during the terminal phase of an immune response, where it has important anti-inflammatory functions to prevent unnecessary tissue damage caused by the immune system. Interestingly, pDC have been reported to control B-cell-derived IL-10 production, which together with the strong effects of IL-10 on pDC activation would fit into the concept of a vicious circle of chronic pDC activation such as described during systemic lupus erythemathosus. Considering the necessity to regulate innate immune responses to avoid damaging effects of IFN-a during infections, it is not surprising that other cytokines such as include prostaglandin E2 and transforming growth factor-b which counter-regulate pDC responses have been described. Their effect on porcine pDC was not addressed in the present study, but we expect a suppression of IFN-a responses as in other species. Taken together, the knowledge on how cytokines regulate pDC responses can be employed to modulate the immune response towards a wanted direction. Considering the importance of type-I IFN as endogenous immunological adjuvant, cytokines could for instance be used to enhance pDC-derived type-I IFN during vaccination. Another area would be to employ such knowledge for immunotherapies of cancer, chronic virus infections and autoimmune diseases where pDC responses can be beneficial or unwanted.Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-d, a member of the ligand-activated PPAR nuclear receptor family.
Category: MAPK Inhibitor Library
As exhibiting an intermediate DEND phenotype and consistent with the gain-of-function phenotype
Second, early discontinuance of lenalidomide maintenance therapy based on an increased incidence of adverse events may influence the statistical power of therapeutic outcomes. Finally, population characteristics, crossover designs with the probable risk of inadequate washout period, differing lenalidomide schedules and dosages, and use of concomitant drugs may have resulted in a somewhat speculative interpretation of our analysis. Also, patients’ ages in the included studies ranged from 22 to 91 years, and efficacy in older individuals is not necessarily the same as in younger individuals. Separate subgroup analysis should be done for older vs. younger adults, but the data needed to conduct subgroup analysis could not be extracted from the studies. Further, because the seven trials we reviewed compared lenalidomide therapy with placebo, and not with thalidomide, no conclusion can be made regarding lenalidomide as first-line treatment over thalidomide. In summary, the findings from our meta-analysis indicate that lenalidomide therapy significantly improves response rates and increases progression-free survival in patients with newly diagnosed MM, and those receiving previous antimyleoma therapy, but it is associated with an increased risk of a number of adverse events. Obviously, pros and cons remain on the clinical efficacy of lenalidomide as first-line treatment for MM.E229 have been reported to form inter-subunit ion pairs and thereby affect the intrinsic open probability of the channel, such that the open probability of mutations E227K and E229K is greater than that of WT channels. Deletion of these residues might also increase intrinsic open probability and we therefore estimated the open probably for these channels, using the ‘PIP2 method’, assessing the increase of channel activity achieved by exposure of excised patches to saturating exogenous PIP2. Two heterozygous mutations, E227K and E229K, located within the deletion region, have previously been studied in detail: in heterozygous expression with WT subunits, both generate channels with a significant right shift in their ATP-response curves. Homozygous E227K and E229K channels also display a higher Po in single channels recordings, consistent with our patch clamp data showing that homDel and homS225T, del channels show higher Po and reduced ATP sensitivity. Interestingly, other mutations at these same residues have been shown to cause rapid current decay due to the loss of inter-subunit interactions. Based on these studies, E229 was proposed to form an ion pair with R314 from the adjacent subunit, such that disruption of this interaction would lead to inactivation. As revealed by the homology modeling in Figure 5B, E227 might also interact electrostatically with R192. Although no molecular mechanism so far has been proposed to explain the higher Po in E227K and E229K mutations, conceivably this may relate to repulsive interactions with R314 or R192. The patient carrying the S225T, del mutation had infancy-onset diabetes, as well as learning difficulties during primary school, and a single episode of seizures at 10 years of age.
Reflex may be an intermediate process for the association between OH and incident CHF
In addition to autonomic dysfunction, some other mechanisms have also been suggested to be involved, such as reduced coronary flow caused by frequent postural BP drop, increased early subclinical atherosclerotic burden, abnormal nocturnal change in BP, and increased longstanding cardiovascular overload. These mechanisms are also needed to be confirmed by future studies. Our stratified analysis indicated that the significant association between OH and CHF incidence can be found in middle-age subjects and those with hypertension and DM at baseline. These results highlight the predictive effect of OH for future CHF in both the low-risk population and the high-risk population with known CHF risks. Although the results were not significant for elderly subjects and those without hypertension or DM, our study still found presence of OH increased the risk of future CHF in these subgroups. In our point of view, these insignificant results may be attributed to the small number of the included studies. Our study has some limitations which should be considered when interpreting the results. First, the number of studies included in the meta-analysis and stratifies analyses is small. The results for some subgroups should be interpreted with caution. Second, the CHF outcomes of the included studies were defined as CHF hospitalization or death. So, some less severe or asymptomatic CHF cases may not be included. Third, our meta-analysis is based on observational studies. Hence, we cannot exclude the chance, residual or unmeasured confounding. However, since there seemed to be no evidence-based effective intervention for the treatment of OH, it is difficult to confirm our results in a large randomized trial. Fourth, potential therapy to OH and many kinds of medications such as antihypertensive reinforces possibility satisfactory therapy await discovery fundamental proximal pathogenesis medication may affect the risk between OH and CHF. However, as indicated in a recent review, many commonly recommended interventions for OH have a limited evidence base supporting their use, and the effects have not been confirmed. Also, effects of some antihypertensive medications on OH, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, are not always consistent. Furthermore, potential treatment for OH was not specified in the included studies, although the use of antihypertensive medications was adjusted in two of the studies when estimating the association between OH and incident CHF. We acknowledged that lack of controlling for potential treatment to OH and other medications is an important limitation of our 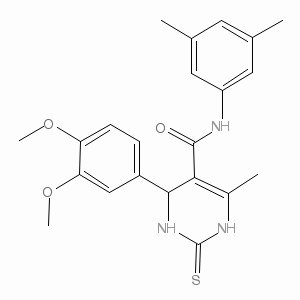 study. Fifth, we did not have data on individual studies to assess CHF etiology or types. Nevertheless, our study also has numerous strengths, including the relative high quality of studies included, a large pooled sample size, robustness of the results in sensitivity analysis, and use trimand-till analysis to handle potential publication bias. In conclusion, results of our meta-analysis confirmed that presence of OH is related to a significant increased risk for development of CHF in the future, especially for the middle-age subjects and those with morbidities such as hypertension and DM. Studies are needed to explore the potential mechanisms underlying this association. More importantly, screen for OH may be of great clinical significance for the early identification of subjects at higher risk for development of CHF. Introduction of new traits into plants via genetic transformation has become an important technology for plant improvement. Proper preservation of transgenes and extension of the new traits to the next generation after the plant growth season are important for the wide use of transgenic technology. Herbaceous plants, especially annual plants, grow once a year. At the end of the growth season, plants die and are disposed, and the transgenes can be lost. However, new genes in plants may be stored and preserved in seeds and then passed to the next generation.
study. Fifth, we did not have data on individual studies to assess CHF etiology or types. Nevertheless, our study also has numerous strengths, including the relative high quality of studies included, a large pooled sample size, robustness of the results in sensitivity analysis, and use trimand-till analysis to handle potential publication bias. In conclusion, results of our meta-analysis confirmed that presence of OH is related to a significant increased risk for development of CHF in the future, especially for the middle-age subjects and those with morbidities such as hypertension and DM. Studies are needed to explore the potential mechanisms underlying this association. More importantly, screen for OH may be of great clinical significance for the early identification of subjects at higher risk for development of CHF. Introduction of new traits into plants via genetic transformation has become an important technology for plant improvement. Proper preservation of transgenes and extension of the new traits to the next generation after the plant growth season are important for the wide use of transgenic technology. Herbaceous plants, especially annual plants, grow once a year. At the end of the growth season, plants die and are disposed, and the transgenes can be lost. However, new genes in plants may be stored and preserved in seeds and then passed to the next generation.
The results can still be inconsistent when different analysis parameter settings for calculation were selected
In summary, it is often difficult to obtain accurate PCR efficiency, which results in possible erroneous estimation of transgene copy number from qPCR. In this study, we present a novel qPCR approach, named standard addition qPCR, to accurately determine transgene copy number. The strategy is to add known amounts of standard DNA to test samples to change fluorescence intensity and Ct values, which is similar to standard addition in quantitative chemical analysis. In this assay, the estimation of PCR efficiency can be bypassed, which is not the case in the previously mentioned approaches. Among the many types of pharmaceuticals, antibiotics receive particular attention concerning their risk to the natural environment. Antibiotics are widely prescribed worldwide, and thus are expected in receiving waters. Their presence in the aquatic environment is of concern as they are potentially harmful to organisms there. They are thought to foster bacterial resistance, for example. Not surprisingly, recent studies on the occurrence of micropollutants in the environment include antibiotics. Several field campaigns have reported fluctuations of pharmaceutical concentrations in receiving waters, the magnitude of which varies with location and substance. Roig reported an extensive overview of different field campaigns focused on antibiotics and other pharmaceuticals in surface waters, including Wastewater Treatment Plant influent and effluent. Since the temporal variation of pharmaceutical concentrations is a supplementary pressure on aquatic system preservation, understanding of such variations is an important challenge in environmental assessment and management. Antibiotics are present in both urban and rural environments. For the latter, their concentrations are often driven by veterinary use. In urban settings, antibiotic concentrations in wastewater result from ambulatory and hospital consumption. As a consequence, consumption data are needed to estimate their concentration. Several studies attempted to estimate wastewater pharmaceutical concentrations using sales data and the Predicted Environmental Concentration Model. These studies were not focused on short-term fluctuations as they considered only annual sales data. At present, no study has considered seasonality in consumption of antibiotics in urban settings. Here, we first investigated seasonality of antibiotic concentrations in wastewater based on monthly sales data and the PEC model. Second, the fraction of antibiotics originating from hospitals in the total load found in 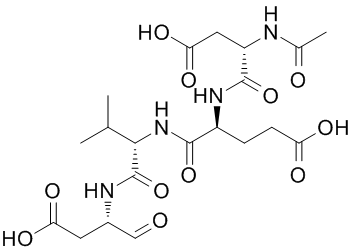 wastewater was examined, again based on monthly consumption. The study considered nine substances – azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, clindamycin, metronidazole, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim – using data for the city of Lausanne, Switzerland. These monthly dry weather wastewater data were provided by Lausanne public authorities. A seasonal trend can be observed with higher volumes in summer than in winter. Similar behaviour in WTP dry weather monthly flow volumes was observed in other studies. In our approach, we considered only hospitals or clinics performing acute somatic treatments, as such establishments dispense antibiotic prescriptions. The study is based on data from ambulatory sales and hospital dispensaries. These data are considered as accurate measures of consumption. Antibiotics are prescription drugs, and are pathology-specific.
wastewater was examined, again based on monthly consumption. The study considered nine substances – azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, clindamycin, metronidazole, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim – using data for the city of Lausanne, Switzerland. These monthly dry weather wastewater data were provided by Lausanne public authorities. A seasonal trend can be observed with higher volumes in summer than in winter. Similar behaviour in WTP dry weather monthly flow volumes was observed in other studies. In our approach, we considered only hospitals or clinics performing acute somatic treatments, as such establishments dispense antibiotic prescriptions. The study is based on data from ambulatory sales and hospital dispensaries. These data are considered as accurate measures of consumption. Antibiotics are prescription drugs, and are pathology-specific.
If our post on Variability of MDD and CRHR1 gene is likely to be involved in the antidepressant response in MDD has actually realized your passion, please see our internet site http://www.inhibitorclinical.com/index.php/2019/02/27/impulsive-patients-showed-lowered-heart-rate-atd-behaving-aggressively/ to learn much more.
Caspase-12 is localized specifically on the cytoplasmic side of the ER and is thought to play a pivotal
Involving synthesis, folding, and posttranslational modification of secretory and membrane proteins. ER stress under any harmful conditions could lead to decrease protein synthesis and increase the expression of molecular chaperones that promote proper folding and cellular recovery. However, prolonged activation of ER stress ultimately initiates the apoptotic pathway. Several proteins have been implicated in this apoptotic pathway, including a transcription factor, C/EBP homologous protein, and the ER-resident caspase, caspase-12. Increasing evidences demonstrated that ER stress may play a critical role in the pathogenesis of many acute and chronic neurodegenerative disorders, such as cerebral ischemia, Alzheimer��s disease, Parkinson��s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Volatile anesthetics could induce neuronal degeneration and apoptosis, then lead to memory impairment. Evidences from animal models suggested volatile anesthetics interaction with neurodegenerative mechanisms, such as the onset and progression of Alzheimer��s disease. Sevoflurane is one of the most commonly used volatile anesthetics and it had been shown to impair long-term emotional memory consolidation in human research, and especially in old mice. But the underlying molecular mechanisms are still unknown. Therefore, we hypothesized that ER stress mediated hippocampal neurons apoptosis then induced neurons lost in the aging brain under long time sevoflurane exposure. It might play a role in the sevofluraneinduced memory impairment in aging rats. Previous studies have shown that volatile anesthetics, such as sevoflurane and isoflurane, are very helpful for reduction of perioperative mortality. But volatile anesthetics may also contribute to memory impairment by neurons lost in hippocampus through cells apoptosis. The Morris water maze test of the present study showed that the sevoflurane group rats showed significantly longer latency to locate the hidden platform than the control group on the training days. it suggested that sevoflurane anesthesia had a significant effect on spatial orientation in the navigation task because it impaired the performance of the sevoflurane group. Meanwhile the number of times that crossing over the previous platform site and the percentage of time swimming in the rats of the sevoflurane group are also decreased that indicating the impairment in memory. The present data also demonstrated that 2% sevoflurane concentration for 5 h exposure would cause neurons apoptosis as the clumped chromatin with fragmentation of the nuclear membrane, verifying apoptotic degeneration under TEM observation. TUNEL staining revealed the same trend that the number of TUNEL positive cells was significantly higher in the sevoflurane group in the hippocampal CA1 and DG region. However, the upstream mechanism of volatile anesthetics induced apoptosis remains unknown. The two most well studied pathways are the cell surface death receptor pathway and the mitochondria-initiated pathway. The study showed that isoflurane might induce caspase activation and apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. ER stressinduced apoptosis became an important pathological event in some neurological disease processes and neuronal cell death. It has been reported that CHOP and caspase-12 are both key mediators of ER stress-induced apoptosis. CHOP is expressed at very low levels under physiological conditions, but strongly induced in response to ER stress.
Do you love discovering www.mapkangiogenesis.com? Check out http://www.proteintyrosinekinases.com/index.php/2019/02/22/formed-majority-sugars-oxidized-sugar-aldonic-acids/.